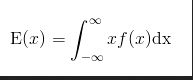Inferential Statistics – Part 1
Introduction: Inferential Statistics :
The process of “inferring” insights from sample data is called “Inferential Statistics”
Basics of Probability:
In the topic we will go through:
- Basic definition of probability
- Multiplication rule of probability
- Addition rule of probability
- nCr (Combinatorics)
Random Variables
Random variables are quantities with distinct characteristics and behavior.
- Random variables are denoted by capital letters
- Random variables are associated with random processes
- Random variables give numbers to outcomes of random events.
A few more example of random variables:
- X = total of lotto numbers
- Y = number of open parking spaces in a parking lot
- Z = number of aces in a card hand
Probability Distribution
A probability distribution is a statistical function that describes all the possible values and likelihoods that a random variable can take within a given range. This range will be bounded between the minimum and maximum possible values, but precisely where the possible value is likely to be plotted on the probability distribution depends on a number of factors. These factors include the distribution’s mean (average), standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis.
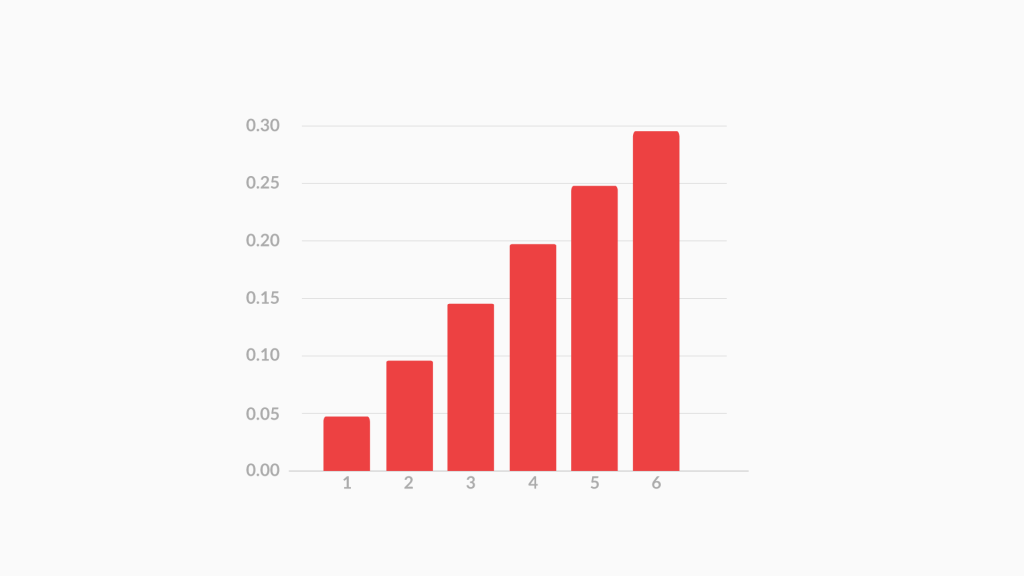
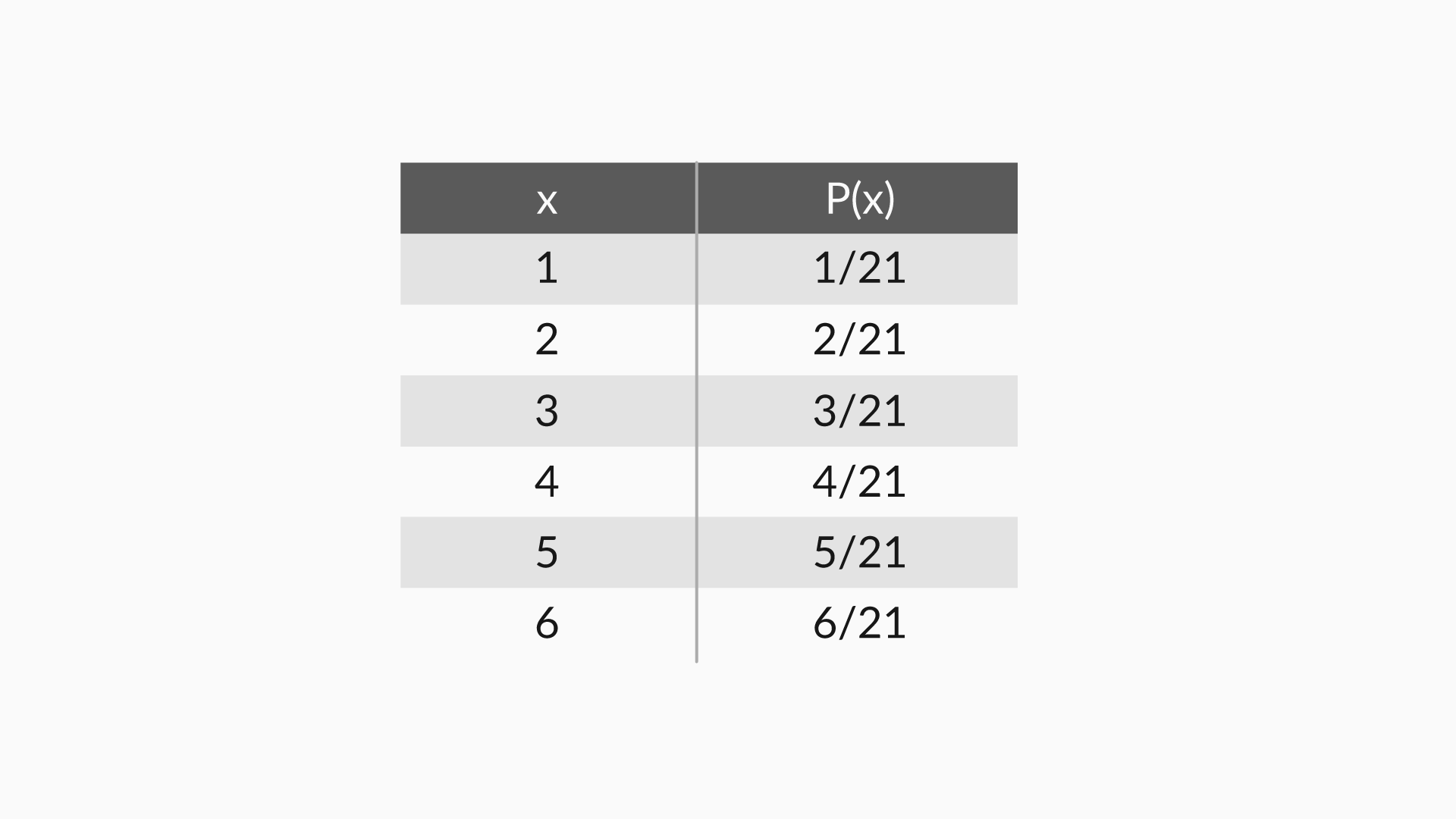
So basically, a probability distribution is ANY form of representation that tells us the probability for all possible values of X. It could be any of the following:
- a Table
- a Chart
- or a simple equation
P(x) = x/21
(for x = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6)
Expected Value
The expected value can really be thought of as the mean of a random variable. This means that if you ran a probability experiment over and over, keeping track of the results, the expected value is the average of all the values obtained. The expected value is what you should anticipate happening in the long run of many trials of a game of chance.
Basic Expected Value Formula
(P(x) * n).
Expected Value of a Binomial Random Variable
P(x) * X.
Expected Value for Multiple Events
E(X) = ∑X * P(X)
The equation is basically the same, but here you are adding the sum of all the gains multiplied by their individual probabilities instead of just one probability.
Expected Value for Continuous Random Variables